Angle Between Vector And Axis In 3d
In the zero case the axis does not matter and can be anything because there is no rotation round it.
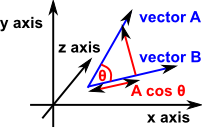
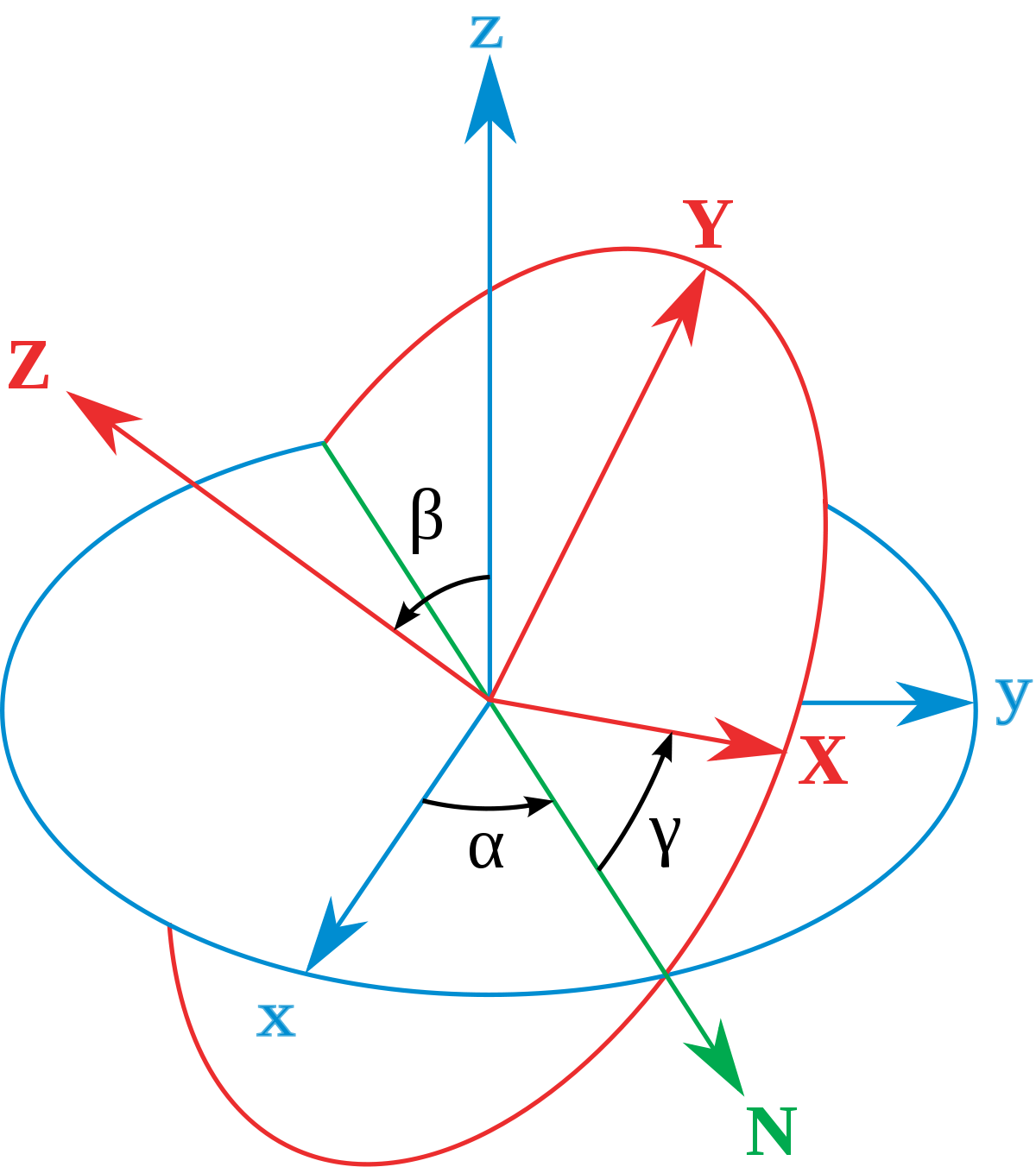
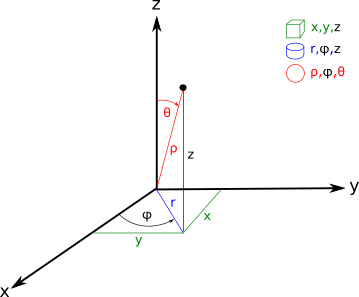
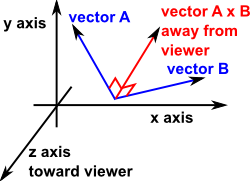
Angle between vector and axis in 3d. Now if in the diagram above α is the angle between u and the x axis in dark red β is the angle between u and the y axis in green and. They are called direction angles. We now zoom in on the vector u and change orientation slightly as follows. If the vectors are parallel angle 0 or 180 degrees then the length of v1 x v2 will be zero because sin 0 sin 180 0.
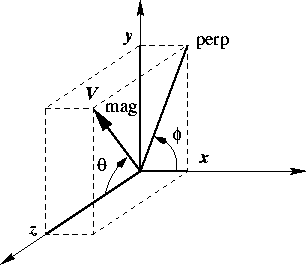
Angle arccos a h so the angle between the x axis and the resultant r which is a 3d hypotenuse is given by angle arccos i r arccos 1 9 3 72 angle 59 3 degrees. In the 180 degree case the axis can be anything at 90 degrees to the vectors so there is a whole range of possible axies. They are always positive and between 0 and 180 inclusive. If vector a makes an angle θ with the x axis then it s direction cosine along x axis is cosθ α.
The cosines of the angles a vector makes with the cartesian coordinate axes are the direction cosines. If i rotate that 3d camera along the y axis the x axis doens t change. The angles are named alpha x axis beta y axis and gamma z axis.